\[ \newcommand{id}[1]{\text{id}\left({#1}\right)} \]
As professional tides bring me into P2P once again and I revisit some classics of the P2P literature, it is disconcerting to realize just how poorly did I really understand some of those things in the past. And one of those things is the expected lookup complexity of Chord [1].
From the outset, the problem seems simple enough. We start with a set of nodes \(O = \left\{o_1, \cdots, o_n\right\}\) that is arranged in a ring (Fig. 1) and to which Chord assigns, for each node \(o_i \in O\), a random non-negative integer id – let’s call it \(\id{o_i}\) – such that \(\id{o_i} \in \left[0, 2^m\right)\) for some natural number \(m\).
Fig. 1 shows a fake network with \(m = 6\) in which all ids are assigned to nodes. This would never happen in practice as the id space is made to be way bigger than the network size, but it illustrates the shape of the network well, and makes it easier to explain how routing – which is the main point here – works.
The Chord protocol guarantees that each node \(o_i\) eventually builds a local routing table, named a finger table, which contains up to \(m\) entries such that the \(k^{th}\) entry in its table points to a node \(o_j \in O\) that has the closest id to \(\id{o_i} + 2^k\), where \(0 \leq k \leq m\)1. Fig. 1 depicts finger tables for nodes with ids \(0\) and \(20\).
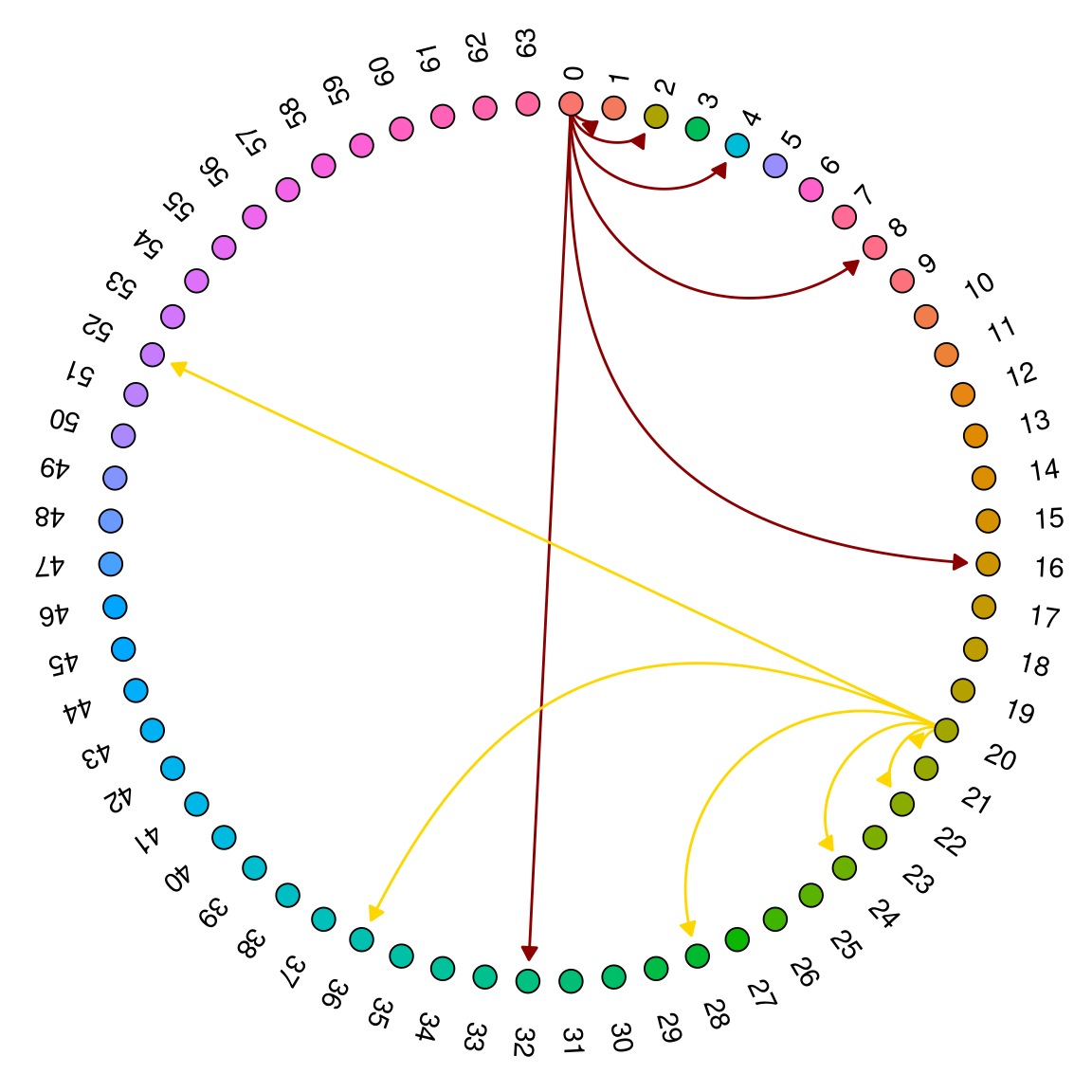
Figure 1: A full-network Chord DHT with m = \(6\)
When a node \(o_a\) wishes to find a node \(o_b\), then, all it needs to do is to lookup the node in its own routing table that has the id that is closest to \(\id{o_b}\). Because of the way fingers are arranged, \(o_a\) is guaranteed to have in its routing table some node \(o_c\) such that \(\id{o_c}\) is at least within a distance of \(2^{m - 1}\) of \(\id{o_b}\).
\(o_a\) can then ask \(o_c\) to repeat this process, and return the node \(o_d\) that it knows to be the closest to \(o_b\). Again, because of the way fingers are constructed, we know that \(o_d\) must have a node in its finger table that has an id within at least \(2^{m - 2}\) of the target. By continuing this process iteratively, it is not difficult to see that, after \(m\) steps, we will necessarily get to \(o_b\) as we will find a node that is within distance \(2^{m - m} = 1\) of it.
And this completes the basic intuition I already had: lookups always take less than \(O(m) = O(\log 2^m)\) steps. Chord, however, makes a more subtle guarantee: namely that lookups take \(O(\log n)\) with high probability for a network with size \(n < 2^m\). And that is the problem we want to get into. Let us put that as a theorem, like the original paper [1] does:
Theorem. With high probability, the number of nodes that must be contacted to resolve a successor query in an \(n\)-node network is \(O(\log n)\).
Proof sketch. Suppose there are two nodes \(o_a\) and \(o_b\) that are part of a network containing \(n\) nodes, such that \(o_a\) is looking \(o_b\) up. Following the reasoning we outlined before and assuming wlog that finger tables are complete, Chord guarantees that \(o_a\) should know a node \(o_c\) such that \(\left(\id{o_b} - \id{o_c}\right) \mod 2^m \leq 2^{m-1}\); i.e. \(o_c\) is within distance \(2^{m-1}\), in id space, of \(o_b\). Note that this is irrespective of the number of nodes \(n\) in the network.
As before, this means once again that, after \(\log N\) forwardings, we are guaranteed to have found a node that is within a distance of:
\[ \begin{equation} 2^{m - \log n} = \frac{2^m}{2^{\log n}} = \frac{2^m}{n} \tag{1} \end{equation} \] of node \(o_b\).
Ignoring rounding issues – and recalling ids are integer valued – this means that there are \(\frac{2^m}{n}\) “vacant” ids between node \(o_c\) and \(o_b\). To prove the theorem, we would have to show that there are \(O(\log n)\) nodes occupying these ids, with high probability. This would mean that, with high probability, there would be a logarithmic number of hops that need to be followed before we reach \(o_b\), thus satisfying the bound. We will appease ourselves, however, with just showing that the expected number of nodes between \(o_c\) and \(o_b\) has to be \(1\); namely, that on average there is only one more hop to follow before we reach \(o_b\).
To see that this is true, let us start by looking at the probability that some random id in the DHT is occupied. Since ids are assigned uniformly at random and there are \(2^m\) such ids, it follows that each id can be occupied with probability \(\frac{1}{2^m}\)2. This means that the probability \(p\) that an id is occupied by one out of \(n\) nodes is given by:
\[ \begin{equation} p = \frac{n}{2^m} \tag{2} \end{equation} \]
We can then treat id occupation as a Bernoulli experiment, meaning that for a given range of \(s\) distinct ids, the probability of having \(k \leq s\) occupied ids follows a binomial distribution \(B(s, p)\). If \(X \sim B(s,p)\), it follows that the expected number of occupied ids between \(o_c\) and \(o_b\) is given by:
\[ \mathbb{E}[X] = s \times p = \frac{2^m}{n} \times p = \frac{2^m}{n} \times \frac{n}{2^m} = 1 \]
which is what we wanted to demonstrate. \(\blacksquare\)
This is not a complete proof, and it sweeps a number of important points under the rug - most notably that ids cannot be occupied twice, and that the expectation being \(1\) may not trivially imply that \(O(\log n)\) bound is satisfied whp. But we will defer the complete proof to another day.